Topics:
- Do I need to enroll in Medicare when I turn age 65?
- When is Open Enrollment for Medicare?
- What happens when I retire from my employer after age 65?
- What is the difference between Traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage?
- What does Medicare Part A cover and how much does it cost?
- What does Medicare Part B cover and how much does it cost?
- What does Medicare Part D cover and how much does it cost?
- What does Medicare not cover?
- What is Medigap Insurance and when should you buy it?
- Considerations When Comparing Traditional Medicare vs Medicare Advantage?
- What are health insurance options for Retirees under Age 65?
- What should I consider when changing plans?
- Available Resources
Do I need to enroll in Medicare when I turn age 65?
When you turn 65, Medicare will become the primary payer unless you are continuing to work and your employer has 20 or more employees. In this case, you may not need to enroll in Medicare, and your employer health coverage generally remains the primary payer. Beginning on January 01, 2025, there are rules in place for insurance carriers to perform a review and calculations to determine if their health insurance plans PASS or FAIL as “creditable.” It is always recommended to check with your HR department or benefits broker to ensure your employer's plan is a "Pass." If not, you will want to enroll in Medicare to avoid late enrollment penalties.
When is Open Enrollment for Medicare?
Medicare open enrollment occurs annually, October 15th through December 7th. This is when Medicare users can choose to re-evaluate part of their Medicare Coverage (Medicare Advantage/Part C and/or Part D Plan) and compare to other plans on the market. After re-evaluating, if there is a plan that better fits one’s circumstances, there is an option to switch, drop, or add a Medicare Advantage and/or Part D plan.
Importantly, members of a Medicare Advantage plan who want to switch back to traditional Medicare after age 66 may not be able to qualify for a Medicare Supplement plan due to medical underwriting. You must first switch from a Medicare Advantage plan to Original Medicare before you can start medical underwriting for a Supplement Plan. As a result, the Medicare participant who wants to transfer after age 66 may have significant out-of-pocket expenses. Due to the underwriting hurdle triggered 6 months after initial enrollment in Medicare Part B, it's important to consider the future desire to have a Supplement/Medigap plan early on when weighing your options.
For those interested in Medicare Advantage Plans, open enrollment is January 1st through March 31st.
The initial enrollment period for an individual approaching age 65 is seven months long. This includes the three months prior to your 65th birthday, the month of your birthday, and the three months following your 65th birthday.
What happens when I retire from my employer after age 65?
If you did not enroll in Medicare because you continued working for an employer that had 20 or more employees but are now retiring, you will have a special enrollment period. The special enrollment period is an eight-month period that begins after the employment ends or your employer's health insurance coverage ends (whichever occurs first).
What is the difference between Traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage?

Source: Medicare.gov
What does Medicare Part A cover and how much does it cost?
Medicare Part A, known as Hospital Insurance, covers the following:
- Inpatient hospital care
- Skilled nursing facility care (if certain conditions are met and coverage is for a limited time)
- Some home healthcare
- Hospice care
- Inpatient psychiatric care
Medicare Part A is considered “premium free” if you or your spouse paid Medicare taxes for a certain amount of time while working.
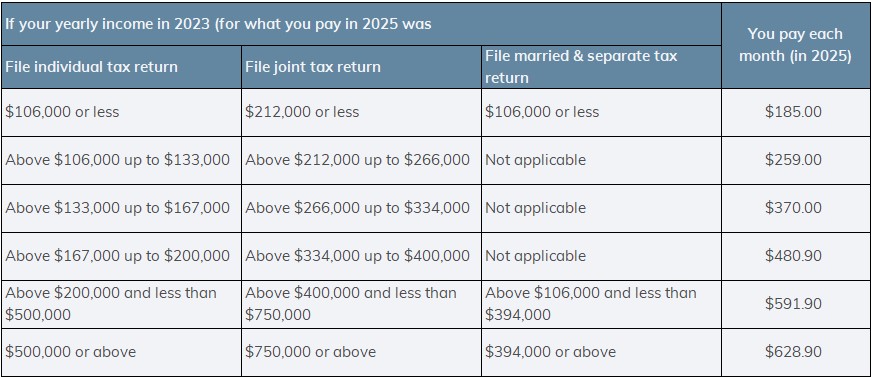
What does Medicare Part B cover and how much does it cost?
Medicare Part B, known as Medical Insurance, covers the following:
- Doctor’s services
- Outpatient services
- Some home healthcare
- Durable medical equipment and supplies
- Certain preventive care
- Ambulance services
- Outpatient medical and surgical procedures
Medicare Part B premiums are automatically deducted from your benefits plan including:
- Social Security
- Railroad Retirement Board
- Office Personnel Management
Medicare uses the Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) reported on your IRS tax return from two years ago. If your MAGI from two years ago was above a certain amount, you will also pay an Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA), which is an extra charge to your added premium.
- Most doctor services (including while you are at the hospital inpatient)
- Outpatient therapy
- Durable medical equipment
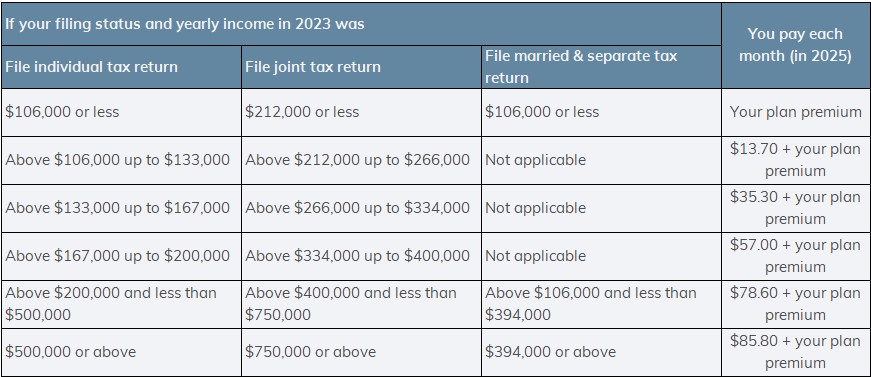
What does Medicare Part D cover and how much does it cost?
Medicare Part D, known as Prescription Drug Coverage, varies by plan. Each plan must give at least a standard level of coverage set by Medicare. Plans can vary the list of prescription drugs they cover (called a formulary) and how they place the drugs into different “tiers” on their formularies.
Medicare Part D premiums are automatically deducted from your benefits plan including:
- Social Security
- Railroad Retirement Board
- Office Personnel Management
Medicare uses the Modified Adjusted Gross Income reported on your IRS tax return from two years ago. If your MAGI from two years ago was above a certain amount, you will also pay an Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA), which is an extra charge to your added premium.
Source: Medicare.gov
What does Medicare not cover?
Medicare does not cover:
- Most dental care
- Eye examinations related to glasses
- Dentures
- Cosmetic surgery
- Acupuncture
- Hearing aids and exams for fitting them
- Long-term care
What is Medigap Insurance and when should you buy it?
Medigap insurance is a Medicare Supplement that covers gaps in Traditional Medicare coverage. Medigap does not cover services not covered by Medicare. You must be enrolled in Traditional Medicare to get Medigap Insurance.
Medigap enrollment is 6 months from the first day of the month of turning 65, assuming one plans to enroll in Medicare. No medical underwriting is required with this initial enrollment period. Exception: for other periods that allow for “guaranteed issue rights” medical underwriting may be required. After age 66, individuals wanting to switch from a Medicare Advantage plan will need to undergo medical underwriting.
Considerations When Comparing Traditional Medicare vs Medicare Advantage?

Source: Medicare.gov
What are health insurance options for Retirees under Age 65?
- Spousal Coverage
- Employer provided retiree coverage
- COBRA
- Affordable Care Act Marketplace
What should I consider when changing plans?
When you are thinking of changing your plan, consider the following:
- Review suitability of Medicare Part D plans each year
- Review suitability of Medicare Advantage plans each year
- Challenges in buying a Medigap policy outside of open enrollment period
- Before disenrolling from a Medicare Advantage plan, find and enroll in a Part D plan and a Medicare Supplement (Medigap)
When comparing available options, consider the following:
- What are the premiums?
- What are the deductibles and coinsurance payments?
- Is there a maximum limit on out-of-pocket costs?
- Are current doctors and hospitals used covered under this plan?
- How often do premiums change?
- Are prescription drugs covered?
- Does the plan offer dental, vision, and/or hearing coverage?
Available Resources
You can find more information on Medicare.Gov. Medicare provides online tools for choosing plans and provides a phone line for support. In addition, please feel free to call us with any questions. If we cannot answer your questions, we can identify a Medicare expert to help navigate this complex landscape. Woodmont Investment Counsel is a fee-only advisor. We do not sell insurance or receive compensation for referrals to insurance agents.
This document contains general information only and is not intended to be relied upon as a forecast, research, investment advice, or a recommendation, offer, or solicitation to buy or sell any securities or to adopt any investment strategy. The information does not take into account any reader’s financial circumstances or risk tolerance. An assessment should be made as to whether the information is appropriate for you with regard to your objectives, financial situation, present and future needs.
The opinions expressed are of the date of publication and may change as subsequent conditions vary. The information and opinions contained in this material are derived from proprietary and non-proprietary sources deemed by Woodmont to be reliable, are not necessarily all inclusive and are not guaranteed as to accuracy. There is no guarantee that any forecasts made will come to fruition. Any investments named within this material may not necessarily be held in any accounts managed by Woodmont. Reliance upon information in this material is at the sole discretion of the reader. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.

